Solving Linear Equations
Example 1
Solve: 3(2x - 6) = -2(x + 4) - 50.
| Solution
Step 1 Remove parentheses.
Distribute 3 and distribute -2.
Step 2 On each side of the equation,
combine like terms.
Combine -8 and -50.
Step 3 Isolate the variable.
Add 18 to both sides.
Simplify.
Add 2x to both sides.
Simplify.
Divide both sides by 8. |
3(2x - 6)
6x - 18
6x - 18
6x - 18 + 18
6x
6x + 2x
8x
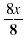 |
= - 2(x + 4) - 50
= - 2x - 8 - 50
= - 2x - 58
= - 2x - 58 + 18
= - 2x - 40
= - 2x - 40 + 2x
= - 40
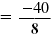 |
| Simplify.
Step 4 Check the solution in the original
equation.
We leave the check to you.
|
x
|
= -5 |
The solution is x = -5.
Note:
We can also solve
6x - 18 = - 2x - 58
by first adding 2x to both sides:
|
6x - 18 + 2x
8x - 18
8x - 18 + 18
8x
x |
= - 2x - 58 + 2x
= - 58
= - 58 + 18
= - 40
= -5 |
The solution of the previous example was a unique real number.
|